Tag: concepts
-

Difference Between W, kW and kWh: Power and Energy Explained
in ExplainersIntroduction In the realm of electrical devices, terms like energy and power often spark confusion. What’s the difference, and how do they relate to the devices we use daily? Let’s explore these concepts, linking them to the units we see on our EEC receipts–kilowatt-hours (kWh)–and on our appliances–watts (W) and kilowatts (kW). Energy vs. Power:…
-

Battery Charger vs Charge Controller: A Simple Guide
in ExplainersIntroduction Two essential components in the realm of battery technology are battery chargers and charge controllers. While their names might sound similar, they serve distinct purposes and play vital roles in ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your batteries. In this guide, we’ll break down the differences between a battery charger and a charge controller…
-

Battery Charging Time: The Difference Between Amps and Amp-Hours
in ExplainersIntroduction Batteries power much of our daily lives, from keeping our smartphones alive to supporting renewable energy systems. Understanding the terms associated with batteries, like amps and amp-hours, can help you make informed decisions about charging and managing your battery-powered devices. In this guide, we’ll explore the relationship between amps, amp-hours, and what it means…
-
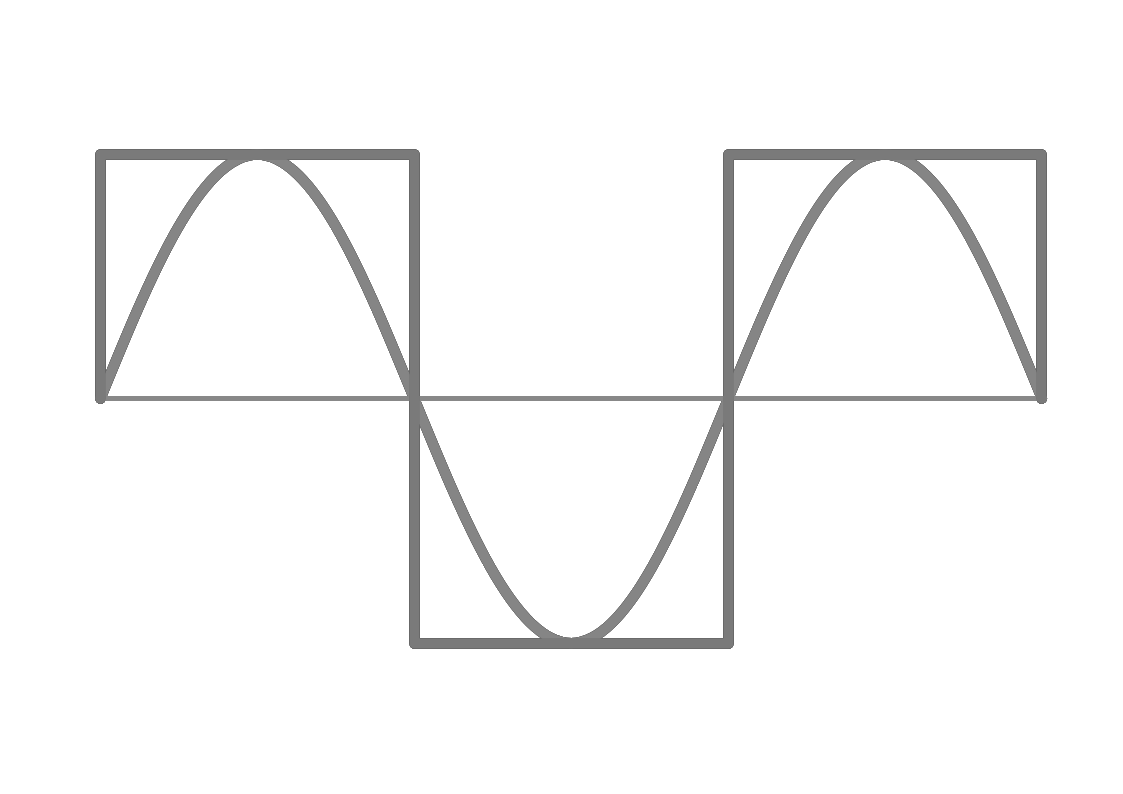
Which Inverter to Choose: Pure Sine Wave vs. Simulated Sine Wave
in GuidesIntroduction All inverters perform the same function: they convert direct current (DC) electricity like the the output of batteries and solar panels into alternating current (AC), which powers anything that plugs into the wall at home. However, not all inverters are created equal. Broadly speaking, there are two main types, pure sine wave and simulated…
-
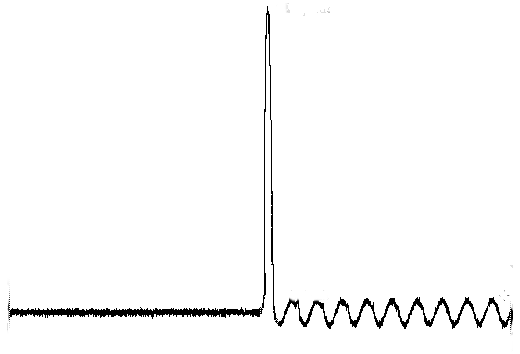
My Inverter Keeps Overloading: Understanding Inrush Current
in ExplainersIntroduction Imagine you’ve just set up your inverter to power your appliances, only for the inverter to beep, indicating that it has detected an oversized load and is switching off to protect itself. You read the nameplate on your device. It says 350W. You read the one on the inverter. It says 500 W max.…